Urticaria Itchy rash testing and treatment in London
Autoimmune urticaria
 Nettle rash or urticaria, as it is more commonly known, is named after the stinging nettle. This is because urticaria looks like the rash you get after touching a stinging nettle.
Nettle rash or urticaria, as it is more commonly known, is named after the stinging nettle. This is because urticaria looks like the rash you get after touching a stinging nettle.
What is urticaria?
One in 20 people are affected by urticaria at some stage of their lives. It often appears like an attack of mosquito bites. Twice as many women as men get urticaria.
Urticaria is acute if it continues daily or almost daily for up to 6 weeks (this pattern may be seen in association with infections or allergy) or chronic if it lasts for 6 weeks or more.
What is urticaria caused by?
In most cases the cause is not found. Urticaria appears when a specialised cell in the skin called the mast cell releases its contents that include histamine. In chronic urticaria, the mast cell is stimulated to do so by your own immune system. Autoantibodies in the body wrongly see the surface of the mast cell as foreign and react with it.
The mast cells are then stimulated to release histamine and other irritating substances that are released into the skin, leading to itching and hives.
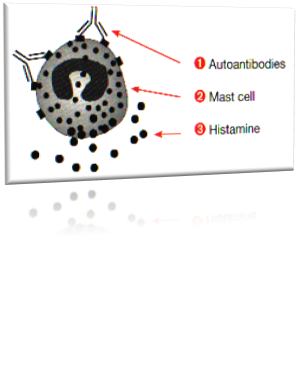
It is now possible to detect these autoantibodies against mast cells in approximately half the patients suffering from chronic urticaria. If autoantibodies are present, there is no need to search for another explanation for the urticaria.
In the remaining patients without detectable autoantibodies the cause of urticaria often remains unknown but, in a few cases, may be due to chronic infections or metabolic disorders.
It should be noted that allergy is hardly ever a cause of chronic urticaria.
Symptoms of urticaria.
are itching, swelling and flushing. The swellings are often pale in the centre and red on the outside. The size of the swellings ranges from a few millimeters to more than 10 cm across. Urticaria can be seen anywhere on the skin.
The autoimmune reaction:
Approximately half of all patients with chronic urticaria suffer from the autoimmune form. Autoimmune urticaria means that auto-antibodies in your immune system 0 react with your own mast cells. The reason they occur is unknown. These auto-antibodies can be detected in your blood by measuring release of histamine from blood cells in the laboratory.
What is the incidence of autoimmune urticaria?
0.1-0.3 % of the adult population is supposed to suffer from the disease. This is comparable to the frequency seen in children. Does autoimmune urticaria indicate a history of allergy?
No, patients with autoimmune urticaria do not have allergy as a cause of it. Allergy can be shown to be the cause of urticaria in only a few cases. However, you will need to visit your doctor to get this confirmed or excluded. The doctor’s assessment may include testing for relevant allergies and auto-antibodies.
The doctor has told me that I have a positive urticaria test for auto-antibodies?
As your disease is not caused by food allergy you should not try to cure it by dieting. Please note that a positive urticaria test in the blood may indicate a more severe and protracted course of your urticaria.
How does the doctor diagnose autoimmune urticaria?
The diagnosis and treatment of autoimmune urticaria is undertaken by a specialist after taking a careful case history and excluding other forms of chronic urticaria.
Testing for chronic spontaneous urticaria
It is generally accepted that the Autologous Skin Serum Test (ASST) tests the reactivity of mast cells to serological histamine releasing factors that causes a wheal and flare reaction in the skin.
However, the outcome of ASST has been proven to be highly dependent on the experience and subjective assessment of the performing doctor or nurse, and as serological factors other than auto-antibodies can also cause a wheal and flare reaction in the skin, a positive ASST test is suggestive but not confirmative of an autoimmune reaction.
Functionality of auto-antibodies can however be tested by the in vitro based serum induced basophil histamine release test HR-Urticaria testing in which serum from the CSU patient is incubated with healthy donor or PBMCs containing 1 to 2 % basophils, and the resulting histamine release is measured
The concordance between ASST and HR-Urticaria test is about 70 % and a positive HR-Urticaria Test has furthermore been shown to be a marker for ciclosporin-responsiveness in patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria.
What treatment is available?
Urticaria can be a very distressing disease that may affect the quality and enjoyment of life so treatment is important. Antihistamines are always the first choice. They reduce the itch and, in many cases, relieve your symptoms. In severe cases of symptoms that persist despite antihistamine treatment the doctor can choose other drugs or combine different drugs. However, it is important to note that drugs relieve the symptoms of urticaria rather than curing it.
Novel research brought new anti-IgE treatment for resistant cases into our practice. This treatment has strict indications and can be performed only in the hospital environment.
For how long time can I expect to have urticaria?
It differs from person to person. Studies have shown, however, that many patients become free of symptoms within 1-5 years. About a third of patients with autoimmune urticaria will still have their disease after 5 years.
